AI-Driven Language Models and Infrastructure Deployment
Note: Even though this post is centered around infrastructure deployment, this general model of using AI agents is applicable to almost any process at all! Will write another post on that subject later.

The Dawn of AI-Driven Infrastructure Deployment
Welcome to the age of AI-enhanced infrastructure! As the integration of AI into our work lives progresses, achieving peak performance now depends on our ability to communicate clearly and execute our vision through a fleet of AI agents.
This blog post will delve into the exciting world of AI-driven Language Models (LLMs) and their potential to predict, detect, and fix errors, streamlining the deployment process. If you haven’t yet embraced AI in your day-to-day, it’s time to catch up!
The AI-Enhanced Infrastructure Deployment Journey: From Code to Deployment with LLM Agents
Once upon a time, in the world of software development, errors in code led to faulty infrastructure deployment, causing headaches for developers everywhere. But with the rise of artificial intelligence, a new era has dawned - an era in which AI-powered Language Models can predict, detect, and fix errors, streamlining the deployment process. In this blog post, we’ll explore an example of how LLM agents can enhance Terraform workflows.
Imagine a world where AI-powered agents work hand-in-hand with developers to create robust infrastructure. This reality is brought to life through LLM agents. Here’s how they can assist in deploying infrastructure using Terraform:
-
The Birth of an Idea: Sending Code to LLM Agents First, the Terraform code is sent to the LLM agent via an API. The agent then predicts the expected outcome of the code execution and saves it for later use.
-
The Roadmap: Executing Terraform Plan The LLM agent takes the reins and runs the ‘terraform plan’ command, which generates an execution plan detailing the infrastructure changes. The output of this command is sent back to the LLM agent for interpretation.
-
The Moment of Truth: Interpreting the Output Based on the output received from ‘terraform plan’, the LLM agent embarks on one of two paths:
a) The Path of Error: - The LLM agent locates the source of the error and consults the documentation for the specific resource/s involved. - With newfound knowledge, it attempts to fix the error and pushes a commit back to the repository with the updated code, restarting the process.
b) The Path of Success: - The LLM agent compares the expected outcome it saved earlier with the interpreted outcome of the ‘terraform plan’ command. - If the two outcomes roughly match, the LLM agent proceeds to execute the ‘terraform apply’ command, deploying the infrastructure changes as planned.
And just like that, the LLM agent has successfully deployed the infrastructure while ensuring minimal errors.
Visualizing the AI-Enhanced Infrastructure Deployment Process
Let’s review the above AI-Enhanced Infrastructure Deployment process with this visual representation:
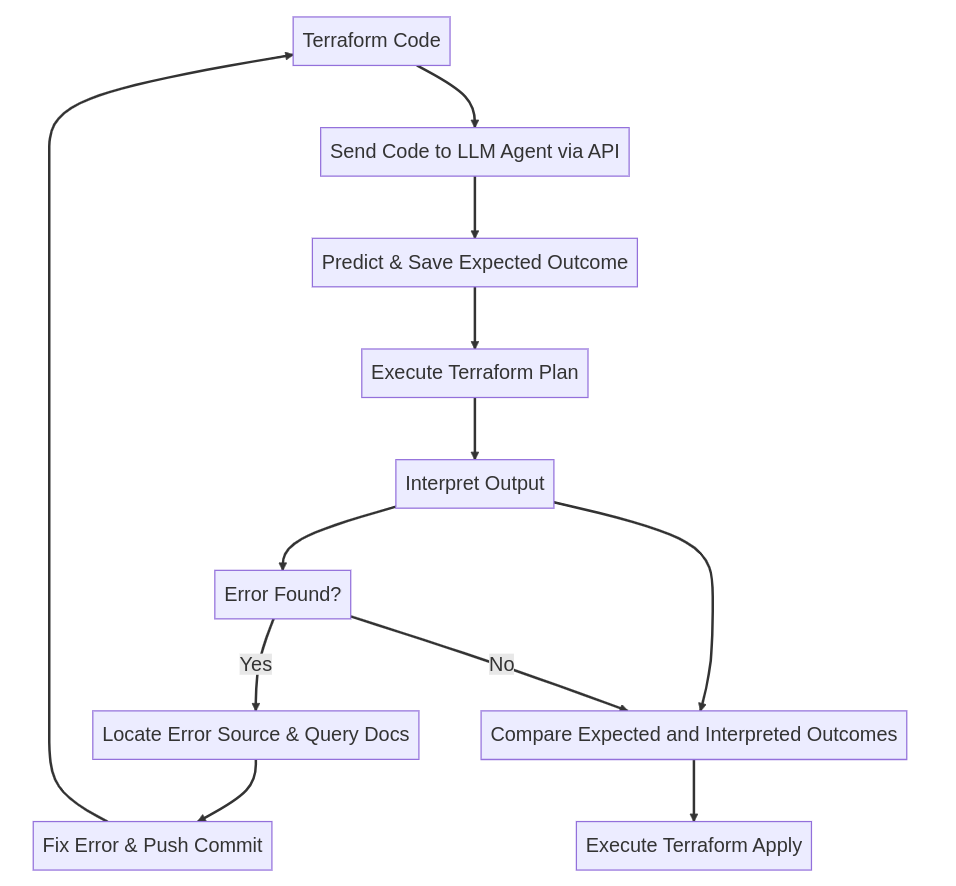
Using a Github Workflow, here’s what the process might look like:
The python script, terraform_llm_agent_workflow.py, might then look something like this:
In the above example, for simplicity I’ve moved all the python functions into a single file to simplify the example, these would easily be split up and run separately.
What does this mean for the world of infrastructure?
The integration of LLM agents into Terraform workflows offers developers a wide array of benefits:
- Reduced errors: LLM agents can detect and fix errors, minimizing the likelihood of deploying faulty infrastructure.
- Faster development: By automating error-fixing, developers can focus on other tasks, accelerating the development process.
- Improved collaboration: LLM agents can bridge the gap between developers, enabling them to work on a shared codebase more efficiently.
Overcoming Challenges and Shaping the Future
Despite the benefits, there are challenges and areas for improvement in incorporating LLM agents in Terraform workflows:
- Limitations of LLM agents: While LLM agents can predict and fix many errors, they might still struggle with complex or unique cases. Developers should remain vigilant and ensure the agents’ proposed fixes are accurate and effective.
As AI and LLM technology continues to advance, we can expect more sophisticated and efficient interactions between agents and Terraform code. The future of infrastructure management is likely to involve increasingly collaborative relationships between developers and AI-powered agents, streamlining the development process and reducing the time and effort required to deploy robust infrastructure.
Several projects are already breaking new ground in the field of LLM agents, such as AgentGPT and Auto-GPT.
The AI-Enhanced Infrastructure Deployment Legacy: A Bright Future for Infrastructure Management
The integration of LLM agents into Terraform workflows offers a promising approach to enhancing the CI/CD pipeline and improving the overall development process. By leveraging AI to predict, detect, and fix errors in the code, developers can focus on other tasks and streamline their workflow. As LLM technology continues to advance, we can expect even more powerful and sophisticated interactions between agents and Terraform code, further revolutionizing the world of infrastructure management.